Project Abstract
Wildfires are increasingly threatening biodiversity and human safety in Europe’s wildland-urban interface (WUI), with delayed tree mortality posing a major challenge for post-fire restoration. A critical challenge in post-fire management is assessing the fate of scorched trees, which may survive initially but die later due to delayed physiological damage. The MAP4FIRE project aims to develop innovative, rapid, and cost-effective tools to assess tree vitality after wildfires, using glucose and ethanol biosensors to integrate visual assessment protocols. Advanced Non-Linear Optical (NLO) microscopy techniques such as Two-Photon Fluorescence, Second-Harmonic Generation, and Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering will be used to characterize morphological, structural, and molecular changes in xylem, cambium, and phloem tissues of fire-affected trees. Field studies at two Italian test sites will validate biosensor performance where prescribed burns and post-wildfire recovery plots are monitored using high resolution dendrometers, remote sensing, visual assessment, and tissue sampling. Additionally, MAP4FIRE will implement Machine Learning (ML) models using biosensor and dendrometer data to predict tree fate and simulate “what-if” post-fire management scenarios via a cloud-based decision support system (DSS). By integrating photonic tools, physiological biomarkers, and AI, the project will support evidence-based decisions in forest restoration and climate resilience strategies, contributing to EU Forest and Biodiversity goals.
Team composition
The transdisciplinary project team includes researchers from two CNR departments (DSSTTA and DSFTM). The CNR’s institutes involved are:
CNR-IRET (Research Institute of Terrestrial Ecosystems, DSSTTA): The institute is involved in research, both basic and applied, on the study of structure, functioning and productivity of terrestrial ecosystems, biotic and abiotic components and their interactions, with a specific focus on global change and anthropogenic pressure.
CNR-INO (National Institute of Optics, DSFTM): pure and applied research in the field of Optics, accompanied by technology transfer, consulting for public institutions and companies, metrology measurements, testing services and training activities.
Key members involved:
Principal Investigator (PI): Alessio Giovannelli (CNR-IRET): Senior researcher and expert in the stress physiology of forest trees, particularly the mechanisms related to their resilience to climate change and recovery from extreme events.
Co-Principal Investigator (CoPI): Riccardo Cicchi (CNR-INO): Senior researcher, head of the biomedical optics research team at CNR-INO and expert in developing optical methods for non-invasive diagnostics, with particular emphasis on non-linear laser scanning microscopy techniques.
Team Member (CNR-IRET): Eleftherios Touloupakis, Senior researcher, expert in the field of biosensor development and of photosynthetic unicellular organisms; Maria Laura Traversi, CNR Technician (CTER), expert of biochemistry of soluble sugars in trees; Alessandro Montaghi, Lead Technologist at CNR-IRET with expertise in software architecture and software development. He has been involved in research in applied informatics and digital agriculture for several years.
Team Member (CNR-INO): Elisabetta Baldanzi, Lead Technologist, Professor of Physics and Psychophysics of Vision (Optics and Optometry). Her research focuses on lighting, colorimetry and vision science. She is coordinator of the CNR-INO Outreach network and contact person for the Press Office.
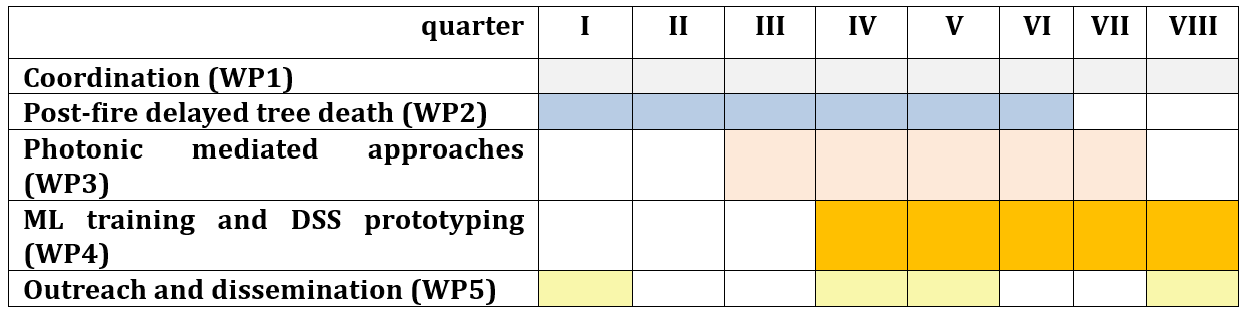
Work package structure
The project is structured into 5 Work Packages:
1. WP1: Management and coordination
○ T1.1. Organization and tracking of the activities of MAP4FIRE through clear lines of communication within the project partners.
○ Lead: CNR-IRET (Alessio Giovannelli), co-lead: CNR-INO (Riccardo Cicchi).
2. WP2: Delayed post-fire tree mortality: exporting results from laboratory to field
○ T2.1: Monitoring test sites.
○ T2.2. Biosensors application for ethanol and glucose determination in phloem sap and visual assessment of scorched trees after wildfire.
○ Lead: CNR-IRET (Eleftherios Touloupakis, Alessio Giovannelli).
3. WP3: Photonic-mediated approaches to assess wood cell damages inducing post fire delayed tree mortality
○ T3.1: Morphological and structural characterization of post-fire tree specimens.
○ T3.2: Molecular characterization of post-fire tree specimens.
○ Lead: CNR-INO (Riccardo Cicchi).
4. WP4: Post-fire delayed Tree death: based model approach development
○ T4.1: Machine Learning algorithms for rule-based prediction.
○ T4.2: Cloud-based Explainable Decision Support System (DSS) for post-fire recovery management.
○ Lead: CNR-IRET (Alessandro Montaghi).
5. WP5: Dissemination and outreach
○ T5.1: Dissemination plan
○ T5.2: Connections with public/private owners
○ Lead: CNR-INO (Elisabetta Baldanzi).
List of Planned Deliverables
● D1.1: Mid-term report (M16 – Month 16)
● D1.2: Final report (M32 – Month 32)
● D2.1: Data set of visual, morphological and biochemical traits related to latent mortality in trees affected by fire from test sites (M12 – Month 12)
● D2.2: User protocol for the glucose and ethanol biosensor for Pinus pinaster trees (M24 – Month 24)
● D3.1: Report on the effect of lethal temperatures on cell integrity and carbon metabolism in the phloem and xylem. (M18 – Month 18)
● D3.2: List of putative biomarkers deriving from fire damage within xylem and phloem to use as proxies of tree latent mortality (M28 – Month 28)
● D4.1: Development of a prototype Decision Support System (DSS) (M24 – Month 24)
● D4.2: User Manual Drafting for the Explainable Decision Support System (DSS) Prototype (M30 – Month 30)
● D5.1: Dissemination plan with a list of the main target groups and related specific activities. (M4 – Month 4)
● D5.2: Report of dissemination activities (workshops – field demos – scientific publications, participation in media programs) (M32 – Month 32)